Project Overview
Vietnam ICU Translational Applications Laboratory (VITAL) Project

VITAL is a unique multidisciplinary project, funded by the Wellcome Trust as part of its Innovations for Impact strategy, providing ICU/critical care innovation in resource-limited settings. The project is a collaboration between The Hospital for Tropical Diseases and Oxford University Clinical Research Unit, in Ho Chi Minh City, the University of Oxford, Imperial College London, King’s College London, ETH Zurich and the University of Melbourne.
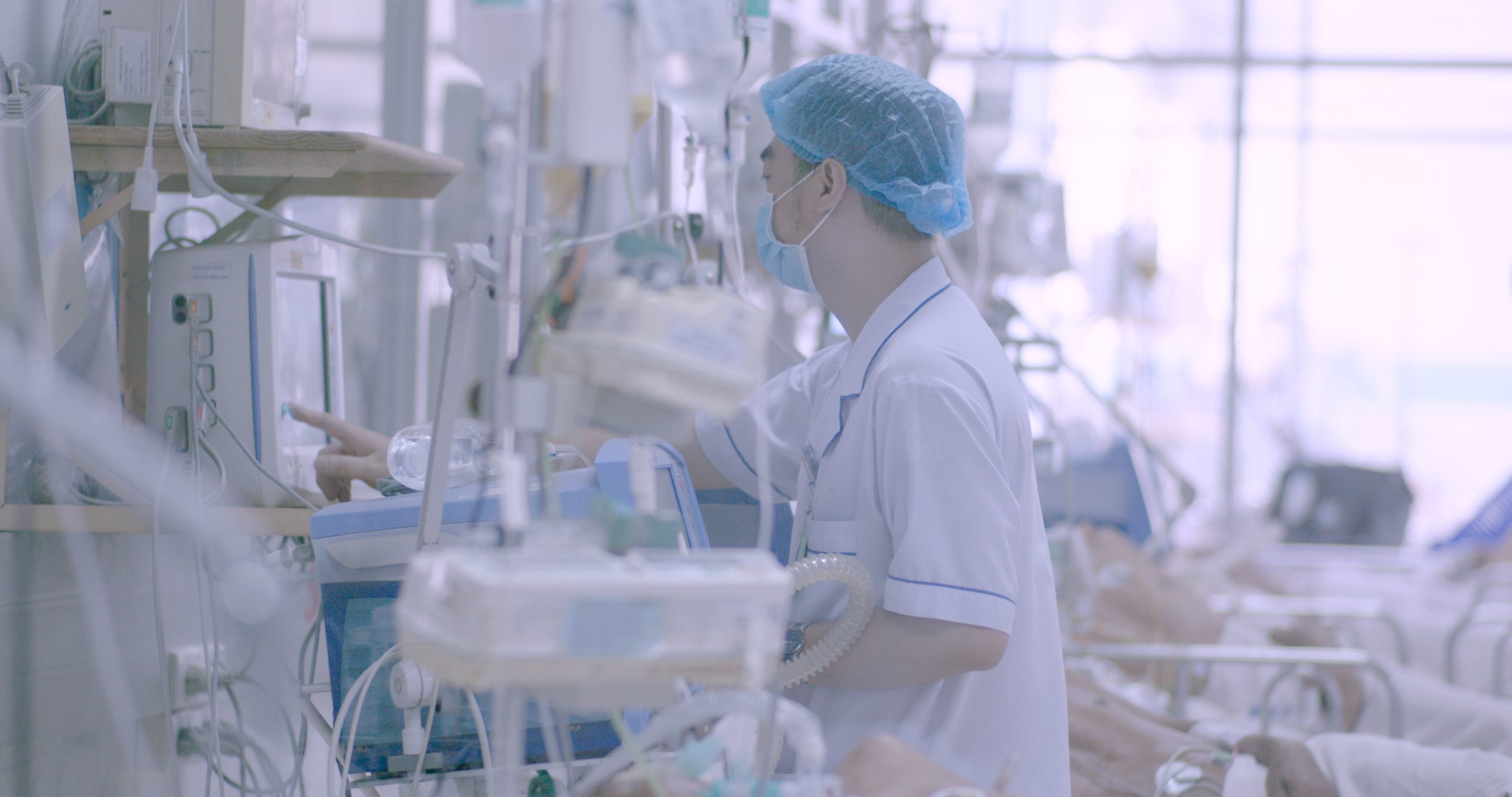
The project brings together clinicians, biomedical engineers, physiotherapists, computational and social scientists aiming to use innovative approaches to improve the care of critically ill patients in low and middle income settings, focusing on diseases which cause significant morbidity and mortality.
The project aims to use state-of-the-art ways to enhance diagnosis and treatment utilizing machine learning, novel technologies and computational science in 4 specific diseases: sepsis, dengue, tetanus and tuberculous meningitis, using low-cost tools that are suitable use in the management of other life-threatening conditions and for scale-up and use in a wider setting. This involves work involving 5 main areas:

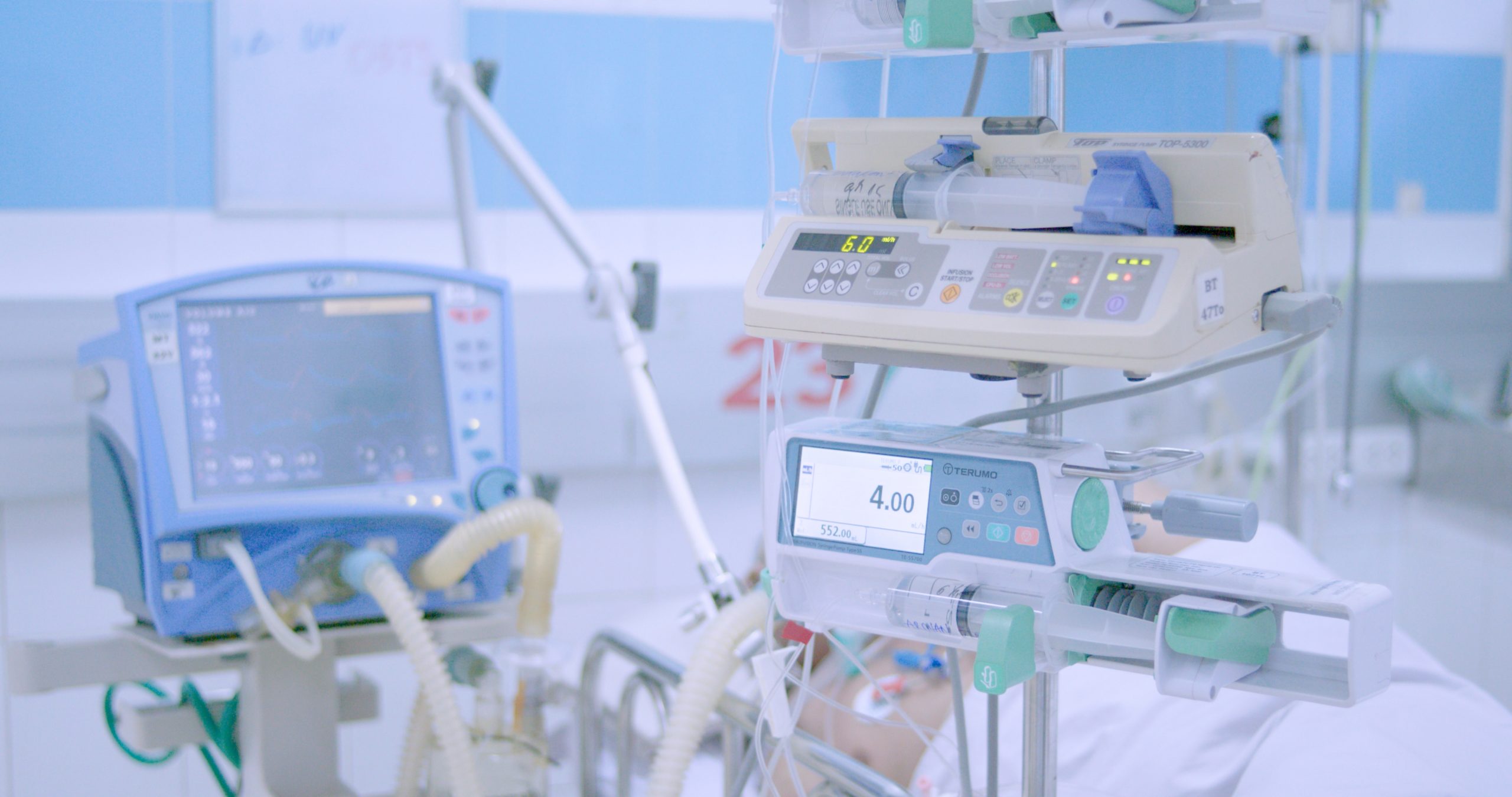
Physiological monitoring: Firstly, we aim to evaluate the feasibility of using lower cost wearable devices to monitor heart rate and blood oxygen as an alternative to costly and conventional ICU monitors. Additionally we will develop new monitoring devices specifically for the diseases common in our setting, for example in dengue we are developing novel wearable sensors and a bioimpedance device to improve detection of disease progression and monitor fluid leakage from blood vessels.
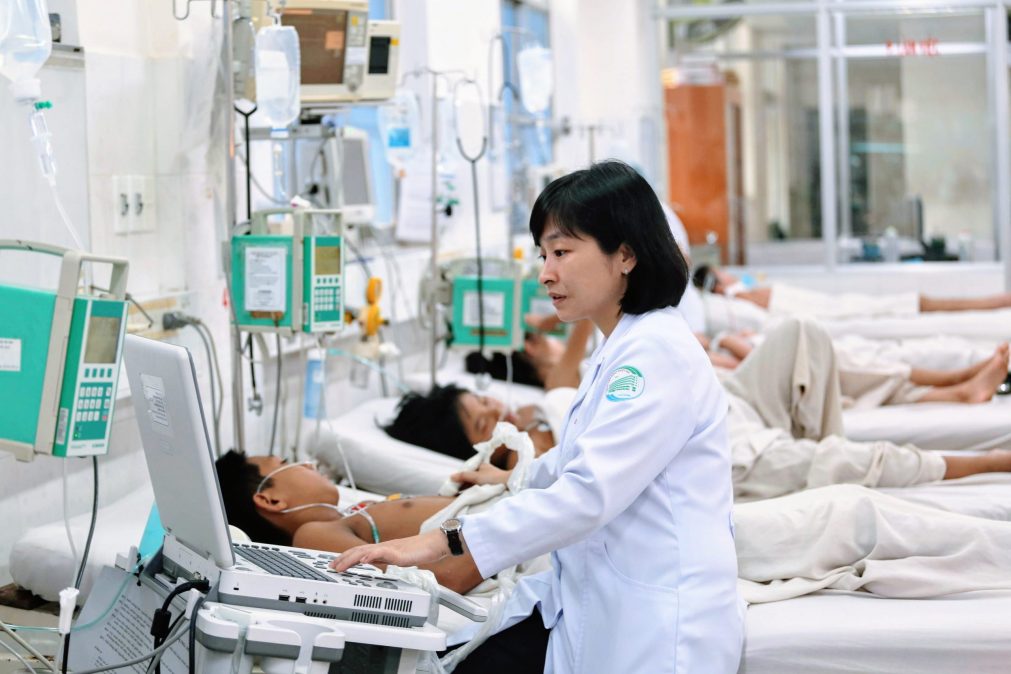


Imaging: The use of imaging, such as MRI scans or ultrasound is often limited by lack of trained people to perform or interpret scans. We are working on ways to enhance the role of imaging in critically ill patients, for example using deep learning to automatically analyze MRI images in TB meningitis. And to help less experienced practitioners carry out and interpret ultrasound scans, focusing on cardiac and lung ultrasound in the management of shock in the ICU.
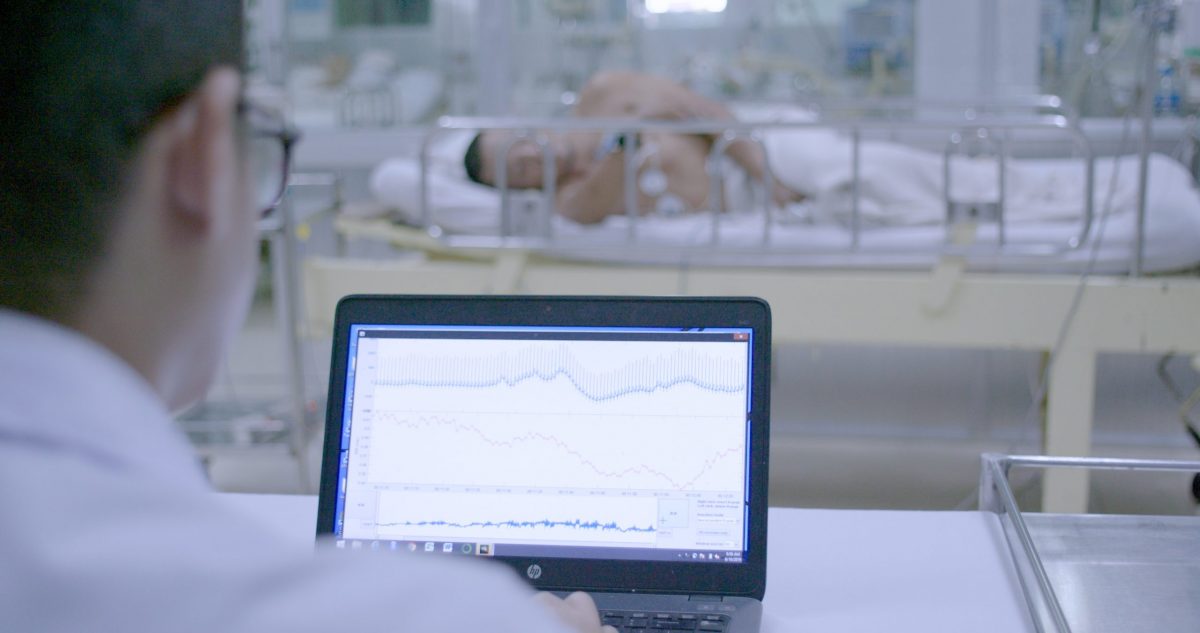

Clinical decision support systems (CDSS): To be able to support busy hospital staff, often working in demanding and crowded conditions, we are developing tools to help medical teams identify patients at risk of deterioration and assist in their management. We plan to use machine learning algorithms and artificial intelligence utilizing simple clinical parameters and monitoring data such as heart rate to develop CDSS in sepsis and dengue.
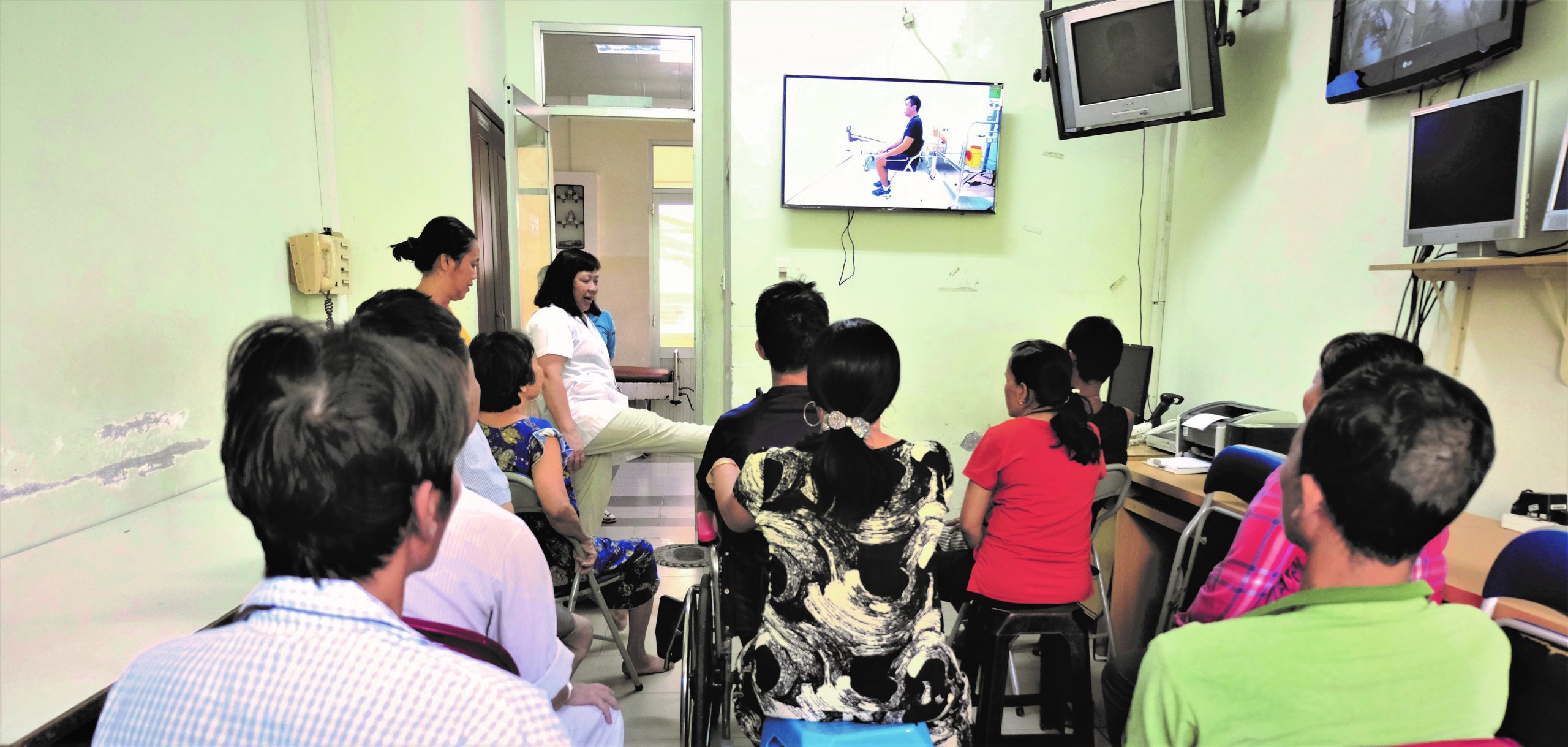

Recovery from critical illness: Highly trained multidisciplinary rehabilitation teams to help patients recover from critical illness are expensive and rarely available in resource-limited settings. We are developing ways to allow non-experts to decide which patients are most likely to benefit from rehabilitation and develop devices and tools to aid this process, for example designing low-cost equipment suitable for use in the ICU and using machine learning to predict which patients can be safely discharged.
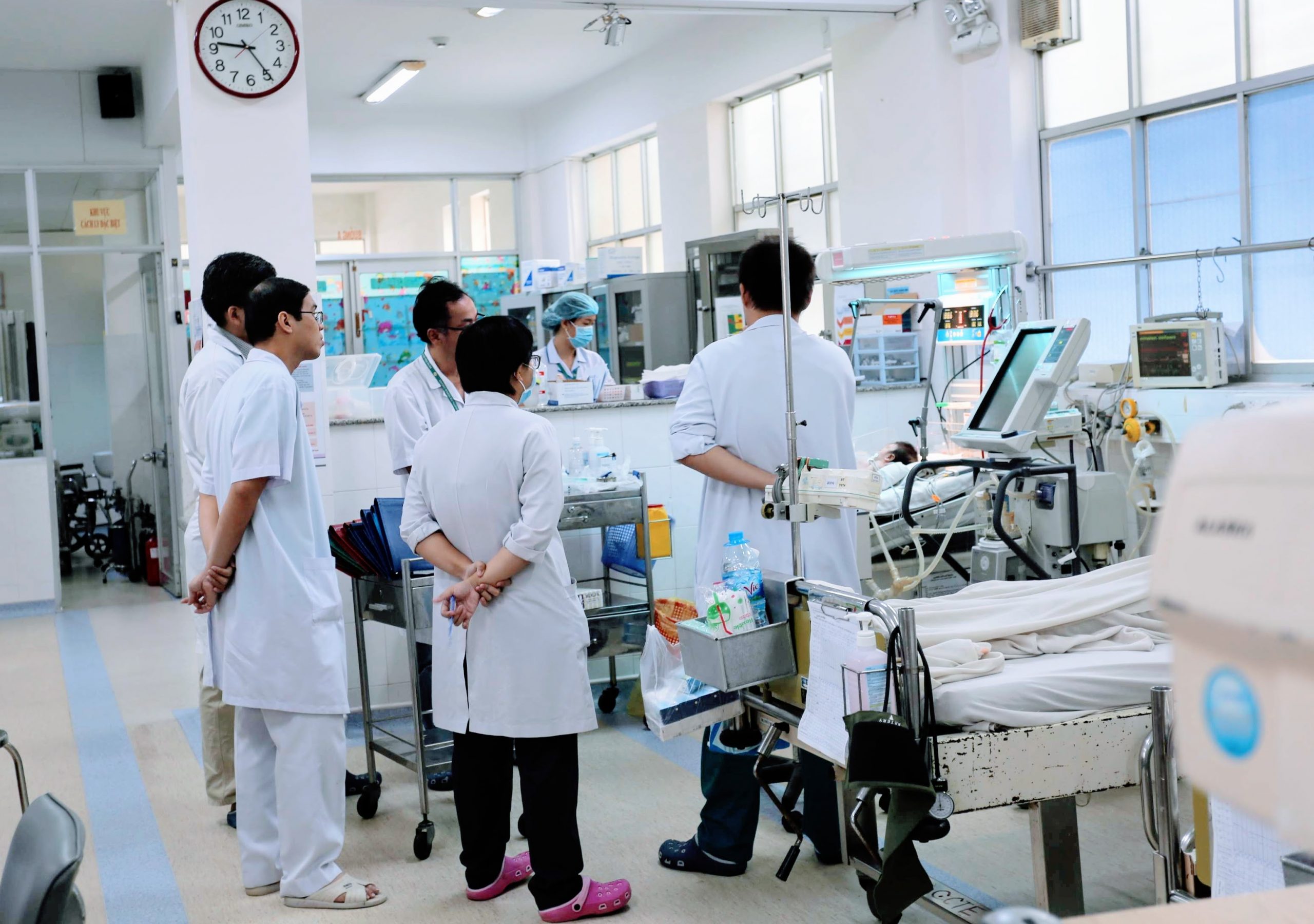


Translation and Ensuring success: To ensure that the innovations are suitable for eventual uptake and scale up, our work will be performed in collaboration with eventual end-users. A dedicated team of researchers will work with policy makers, clinical staff and patients to understand what are the most important features required and how our innovations will function within the wider healthcare landscape of the country and region.
The VITAL project has 5 main themes, each with sub-themes and designated leaders that will address the project aims.
Monitoring

Developing new devices, or testing existing devices, including point-of-care ultrasound, that will enable lost-cost capture and monitoring of key clinical and physiological variables in critically ill patients.
Decision Support

Using artificial intelligence and computer-assisted and machine learning to devise clinical decision-support systems (CDSS) from clinical, physiological, and imaging data.
Rehabilitation
Investigating whether interventions such as in-bed cycling and rectus femoris ultrasound can aid physical rehabilitation within ICU, and whether low-cost wearable devices can promote or predict better functional recovery after critical illness.